
“Affinity-Bead-Assisted Mass Spectrometry (Affi-BAMS) can simultaneously profile various proteins and applicable to all types of biological samples”
By: Vladislav Bergo, Ph.D. CSO, Adeptrix Corp,
Proteomic studies critically rely on multi-dimensional separation methods such as 2D-LC to simplify the complexity of enzymatically digested biological specimens before subsequent MS & MS/MS to efficiently monitor multiple proteins of interest. The time and expertise required to implement LCMS methods can often be a barrier to using targeted proteomic applications in translational research.
Therefore, Adeptrix Corp (Beverly MA) has developed a novel microarray analytical technology termed “Affinity-Bead Assisted Mass Spectrometry” (Affi-BAMS), which integrates multiplex immuno-affinity capture with MALDI-TOF MS to create customized targeted proteomic assays for a wide range of research areas including oncology, neurobiology, epigenetics and virology. They have demonstrated efficient monitoring of multiple histone epigenetic modifications (e.g. H3K9acet) and several core Alzheimer’s disease pathological biomarkers including tau and amyloid beta peptides with a sensitivity greater than that of LCMS methods.
The Affi-BAMS workflow uses enrichment on a single bead that contains one type of antibody while having enough binding capacity to enable quantification within 3 orders of magnitude. The multiplexing capability is achieved by combining Affi-BAMS beads with different specificities. Both intact proteins and protein fragments can be monitored by Affi-BAMS.
How it works?
The Affi-BAMS assay workflow combines three common bio-analytical technologies: magnetic beads, microarrays and MALDI TOF MS to uniquely provide scalable detection and quantification of multiple protein targets in a miniaturized, multiplexed single-bead format. Biological input material is lysed and digested with a protease; the resulting peptides are captured by antibody-conjugated magnetic beads in a bead suspension format. An array is formed from the reacted beads on a microwell array plate. The bead array is exposed to an aerosol containing solution of a MALDI matrix, which causes the bound peptides to be eluted from the spatially separated beads into their respective microwells. The solvent is allowed to evaporate, which causes the eluted peptides to co-crystallize with the MALDI. The silicone gasket is removed to expose the array of spots, which is subsequently measured by MALDI MS and analyzed to identify peptides present in individual spots and to extract quantitative data that is used to calculate abundance changes of corresponding precursor proteins.
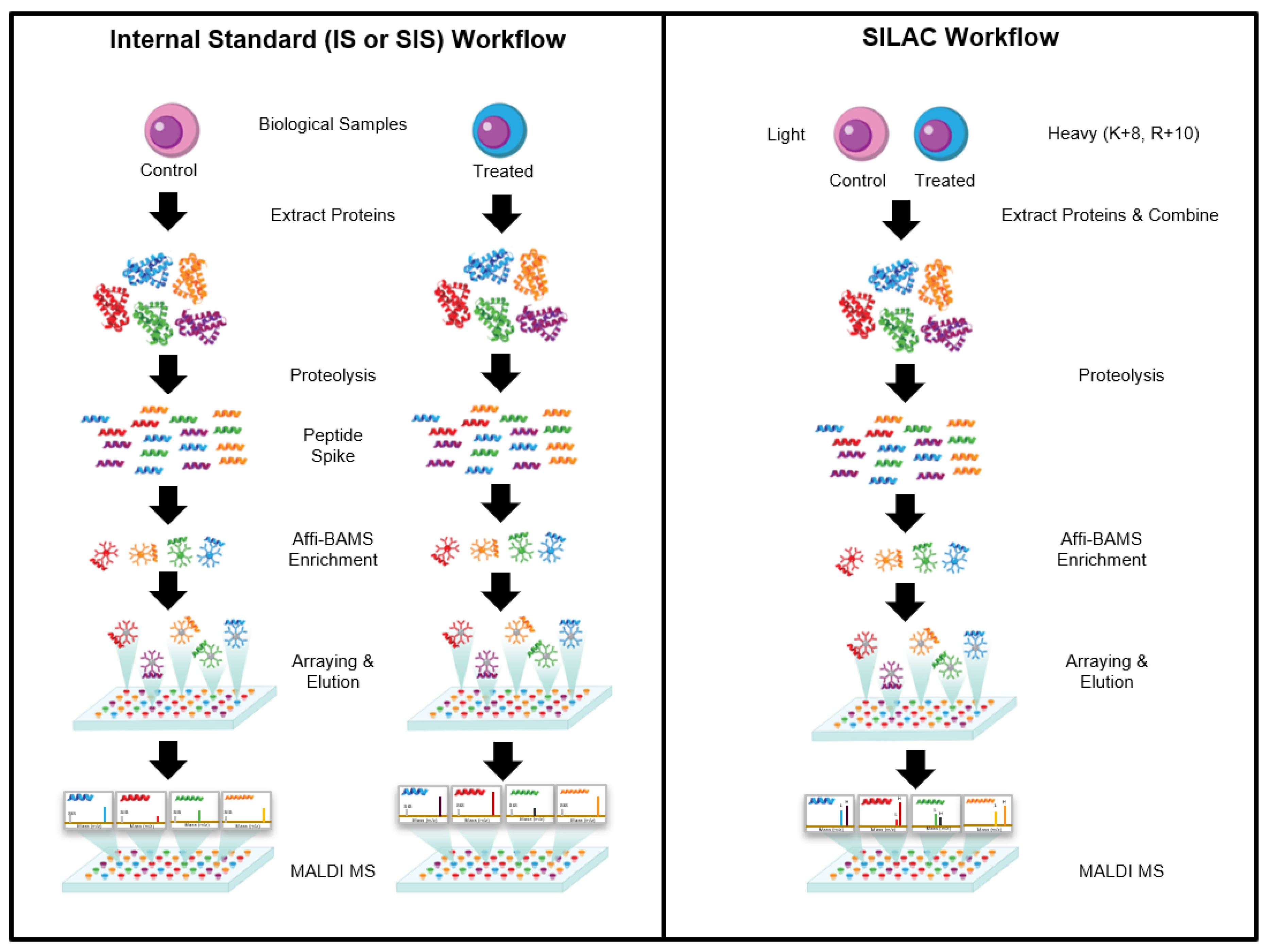
Affi-BAMS Assay Beads and Slide Arrays
Each Affi-BAMS bead includes a covalently coupled antibody that is validated to specifically capture a proteolytic fragment of a target protein (or PTM). The agarose beads contain a magnetic particle core to assist with bead manipulation during the sample preparation. Individual beads have a diameter of about 375 µm. The companion gasket contains microwells with dimensions that are slightly larger than a single bead (500 µm depth and diameter) to ensure one bead per well occupancy.
Peptide Preparation and Enrichment on Target-Specific Immuno-Affinity Beads
For Affi-BAMS assays, peptides are prepared using the standard bottom-up proteomics methods. Under denaturing conditions, 100–200 µg of total protein extract from a cell culture, tissue or liquid biopsy is subjected to reduction, alkylation and proteolytic digestion. Immediately after digestion, proteolytic peptides can be assayed directly for liquid biopsy samples or they can be C18 purified for cell line or tissue samples prior to Affi-BAMS enrichment. Purified peptides are lyophilized and stored (−80 °C) until needed for Affi-BAMS assay.
A single-plex Affi-BAMS assay contains 2-3 replicate beads conjugated to an antibody that recognizes a specific protein target. A multiplexed Affi-BAMS assay contains a mixture of beads conjugated to different antibodies to carry out simultaneous enrichment of multiple protein targets. Affinity capture of target peptides is typically done for 12 h at 4 °C but can be performed within as little as 3 h. Non-specifically bound peptides are removed by a series of brief washes with PBS, ammonium bicarbonate buffer and deionized water.
Bead Arraying, and Conversion to an Array of Peptide Micro-Spots
The microwell array plate for assaying the reacted beads includes a silicone elastomer gasket containing an array of through-holes, which is attached to a gold-coated glass microscope slide. The number of wells exceeds the number of beads used in the affinity assays to ensure that every bead is singularly deposited. A multi-chamber frame serves to sub-divide sets of microwells for the parallel processing of multiple sample sets. The number of chambers that can be accommodated on a single slide is between 1 and 64.
Washed Affi-BAMS beads containing bound target peptides are transferred into the sample chamber wells using a magnetic bead picker, dispersed within chamber wells by gentle agitation and then settle into individual gasket microwells by gravity. The multi-chamber frame is subsequently detached and bulk water is removed from the array surface using a slide spinner.
The bead array is then exposed to an aerosol containing cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (CHCA) in 50% acetonitrile and 0.4% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), generated by a matrix sprayer. The low pH of the solution dissociates bound peptides from each bead, while the sidewalls of the micro-well gasket prevent the possible diffusion of eluted peptides into adjacent wells. Following the elution cycle, the residual solvent evaporates, and the eluted peptides co-crystallize and are incorporated into MALDI matrix in confined spots at the bottom of the micro-wells. Once the matrix is dry, the silicone gasket is lifted off the slide and any remaining dry agarose beads are removed using a gentle burst of compressed air. Via this process, an array of micro-spots containing purified and concentrated target peptides is generated for subsequent MALDI MS measurement.
MS Data Acquisition
Arrays of peptide micro-spots can be measured on any MALDI MS instrument equipped to accept standard 25 × 75 mm microscope slides. The pattern of spots forms an array of 26 × 88 spots (with 0.8 mm spacing between each spot) that can be interrogated via MALDI MS. MS spectra are acquired sequentially from each spot in positive (or negative) ion mode. The laser beam is typically focused to approximately 10–20% of the diameter of the spot to ensure that the individual targets are sampled without contamination from adjacent spots. A MALDI MS instrument operating at 2 kHz speed can analyze a single 500 µm spot in less than 1 s and an entire 2288-spot array within approximately one hour.
Affi-BAMS is highly effective at quantitating specific PTMs, such as phosphorylation, acetylation and methylation, and can be configured to readily distinguish and quantitatively measure protein isoforms and orthologues. This platform can be readily adjusted to a multiplex assay using a defined panel of immuno-affinity beads (i.e., focused target set) for large numbers of samples. The latter is advantageous for monitoring multiple biomarkers in high-throughput screening applications.
- Hamza GM, et al Affinity-Bead Assisted Mass Spectrometry (Affi-BAMS): A Multiplexed Microarray Platform for Targeted Proteomics, International Journal of Molecular Sciences (2020) 21(6): 1-36 (https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/6/2016)
- Silva JC, et al A Targeted Multiplexed MALDI MS Assay Platform using Affinity-Bead Assisted Mass Spectrometry (Affi-BAMS) for Monitoring Brain and CSF Biomarkers, In The Association of Biomolecular Resource Facilities (ABRF) Annual Meeting, Palm Springs, CA, USA, March 3rd, 2020.
- Hamza GM, et al From Chemical Proteomics to Translational Chemical Biology, In Chemical Biology in THE HUB Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, Merck Research Laboratories, September 19th, 2019.
- Mamaev S, et al A High-Throughput Multiplexed Assay Platform for Monitoring Protein Abundance in 96-Well Cell Cultures or Product Profiles from Enzyme-Substrate Reactions, In Proceedings of American Society for Mass Spectrometry 67th Annual Meeting, Atlanta, GA, USA, June 2-6, 2019.
- Mamaev S, et al Bead Assisted Mass Spectrometry (BAMS™): An Affinity Capture MALDI TOF MS Method for Multiplexed Biomarker Screening, In Proceedings of American Society for Mass Spectrometry 66th Annual Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, June 3-7, 2018.
- Mamaev S, et al A Robust Affinity Capture, MS Method for Multiplexed Biomarker Profiling, In Proceedings of American Society for Mass Spectrometry 66th Annual Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, June 3-7, 2018.
Exemplary Affi-BAMS Assays: Monitoring Brain and CSF Biomarkers


Contact Information:
Jeffrey C. Silva, Ph.D.
Adeptrix Corporation
Director of Product Development
100 Cummings Center, Suite 438Q Beverly,
MA 01915
Office: (978) 473-7670
email: jsilva.adeptrix@gmail.com
email: jsilva@adeptrix.com
www.adeptrix.com









Leave a Reply